The Lagos Digital Highway is transforming Africa’s largest city by addressing traffic issues, poor connectivity, and outdated services. Here’s what you need to know:
- Fiber-Optic Expansion: By 2027, Lagos will have 3,728 miles (6,000 km) of fiber-optic cables, improving internet access and reducing costs for residents and businesses.
- Smart Traffic Management: High-tech cameras and AI systems monitor traffic, enforce laws, and reduce congestion, with fines for violations like speeding and red-light running.
- Job Creation: Thousands of jobs in tech and infrastructure are being created, supported by training programs for young professionals.
- Digital Services: Residents now have 24/7 access to online government services, streamlining processes like taxation and permits.
- Economic Boost: Improved connectivity is lowering costs for businesses, enhancing logistics, and supporting tech startups with grants and infrastructure.
This initiative is modernizing Lagos, making it safer, more efficient, and better connected, while driving economic growth and creating opportunities for millions of residents.
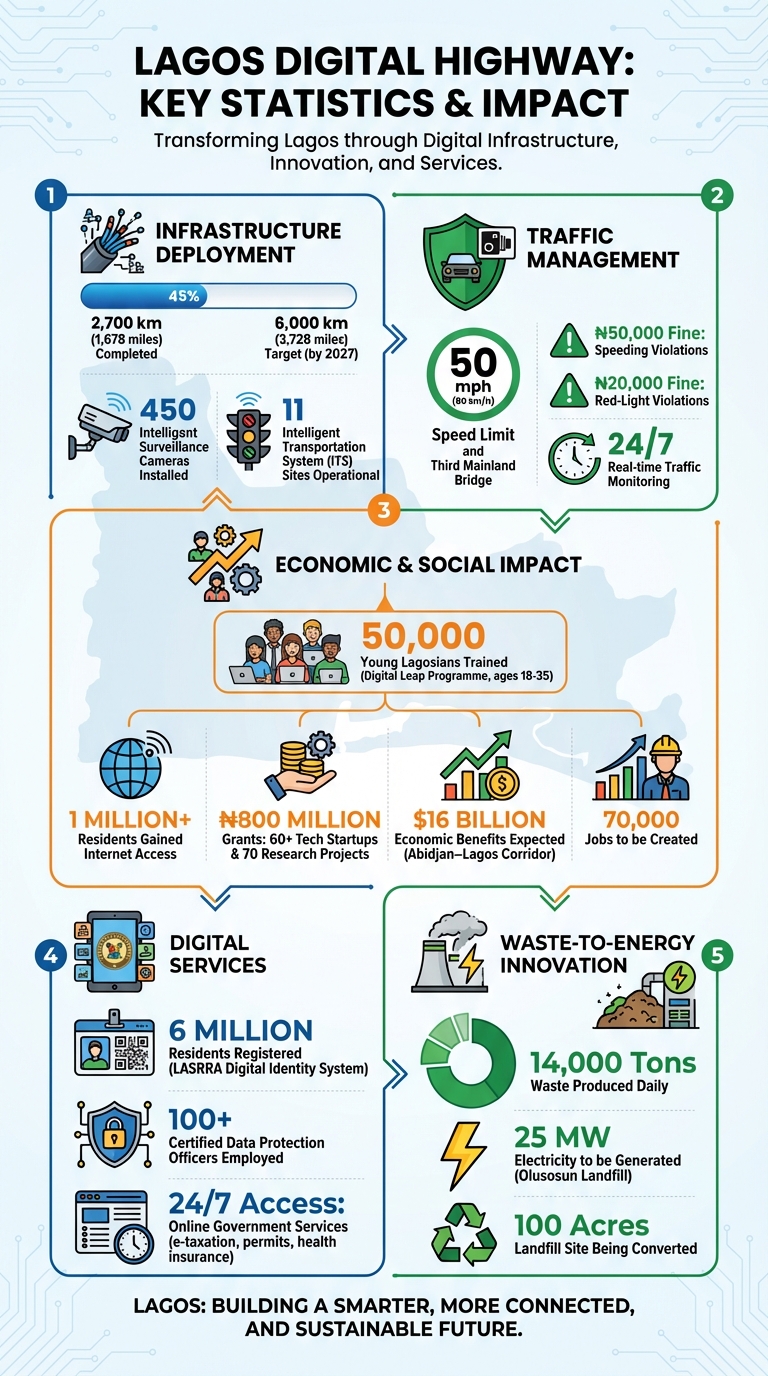
Lagos Digital Highway Key Statistics: Infrastructure, Jobs, and Economic Impact by 2027
How the Digital Highway Changes Traffic Management
Smart Surveillance and ITS Integration
Lagos is embracing a high-tech approach to traffic management with the introduction of smart surveillance cameras as part of its Intelligent Transportation System (ITS). These cameras operate 24/7, observing traffic flow and spotting congestion in real time. Thanks to the Metrofibre Project‘s fiber-optic network, this system ensures constant monitoring across the city.
In February 2025, the Lagos State Ministry of Transportation launched four new ITS sites at key locations: the Allen Avenue junction, Nurudeen-Oluwopopo Road, Alapere-Ogudu Road, and the Nitel junction on Mobolaji-Bank-Anthony Way. These sites are equipped with high-definition cameras and advanced analytics to instantly detect congestion and speeding violations. Additionally, the Third Mainland Bridge received a ₦40 billion CCTV control center to monitor safety conditions.
"The goal is to alleviate traffic congestion and improve road safety. With the Intelligent Transportation System, drivers receive real-time traffic updates, allowing them to plan smarter routes and avoid delays." – Oluwaseun Osiyemi, Lagos State Commissioner for Transportation
By integrating this advanced surveillance, Lagos is laying the groundwork for automated enforcement measures that are reshaping traffic management.
Traffic Violations and Automated Enforcement
One of the standout features of this system is its ability to capture traffic violations without requiring officers to physically stop vehicles. In January 2026, Lagos State teamed up with Huawei Technologies to deploy speed-enforcement cameras on the Third Mainland Bridge. These cameras use Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) technology, which scans license plates and matches them with a database. Offenders receive an SMS notification detailing their fine – ₦50,000 for speeding and ₦20,000 for red-light violations or similar offenses.
The system enforces a strict 50 mph (80 km/h) speed limit on the Third Mainland Bridge using radar, LIDAR, and sensor loops. Beyond speed monitoring, "e-police" sites at locations like Allen Avenue are designed to catch red-light running, illegal U-turns, lane violations, and reverse driving. Once a violation is recorded, the Vehicle Inspection Service (VIS) reviews the evidence at a central processing center before issuing fines.
This automated approach not only ensures compliance with traffic laws but also streamlines enforcement, making daily commutes smoother and safer.
Impact on Daily Commutes
The implementation of automated enforcement has significantly reduced the need for physical traffic stops, which often caused additional congestion. Drivers now benefit from real-time traffic updates, helping them choose less crowded routes and avoid delays. The constant flow of data to traffic authorities also allows for quicker responses to accidents or vehicle breakdowns.
During November 2025’s Operation Ember Months Stability, Lagos State Traffic Management Authority (LASTMA) stationed personnel around the clock on major routes, including Ikorodu Road, Apapa–Oshodi Expressway, and the Lekki–Epe corridor. They worked to clear obstructions and ease the holiday traffic flow. By combining smart surveillance, real-time data, and coordinated enforcement, these efforts aim to reduce travel times and improve road safety for Lagos residents.
Building Better Data Infrastructure
Real-Time Traffic Data Collection
Lagos has built a round-the-clock data network that uses a combination of advanced sensors and cameras to monitor traffic flow and vehicle speeds in real time. This system operates through the expansive 3,300-km (2,050-mile) Metrofibre network, ensuring constant data collection across the city’s roads. In February 2025, the Ministry of Transportation introduced Huawei’s Traffic Management Solution at four critical Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) sites. These sites stream real-time traffic data to a central analytics hub, creating a foundation for forecasting congestion.
Predictive Congestion Modeling
By combining historical data with real-time updates, Lagos’ traffic system can predict where and when congestion will occur, especially during peak hours. This predictive capability allows city planners to reallocate resources efficiently and notify drivers through mobile apps and digital signage. For logistics companies and delivery services, this means they can plan routes based on actual traffic predictions instead of relying on estimates, improving reliability. Commuters also benefit, as they can anticipate delays and adjust their routes accordingly. These insights not only ease daily commutes but also improve the overall management of city traffic and public services.
Integration with Public Services
The Metrofibre Project’s second phase has connected government operations to the Lagos Digital Services Platform, offering instant access to essential services and faster emergency responses. For example, when accidents occur, the system immediately notifies emergency teams, potentially saving lives. Additionally, this infrastructure supports the Vehicle Inspection Service (VIS), which processes traffic violations centrally. Offenders receive automated SMS notifications of fines – ₦50,000 for speeding and ₦20,000 for running red lights.
To safeguard this critical infrastructure, Lagos has employed over 100 certified Data Protection Officers across government departments. These officers ensure adherence to data protection laws while maintaining the system’s reliability. This advanced data infrastructure plays a key role in Lagos’ digital transformation, enhancing urban safety and creating new opportunities in the tech industry.
Smart City Technology Integration
AI and IoT for Urban Development
Lagos has teamed up with Huawei Technologies to roll out an AI-powered infrastructure that forms the backbone of its smart city ambitions. In March 2025, under the leadership of Commissioner of Transportation Oluwaseun Osiyemi, the Lagos State Government completed the installation of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) at 11 key locations across the city. These ITS sites use Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) and advanced sensors to automate traffic enforcement. Fines for violations include ₦20,000 (about $13) for running red lights and ₦50,000 (about $33) for speeding.
"The newly established ITS sites are divided into two main categories: checkpoint sites for speed monitoring and e-police sites for traffic violation detection. These systems are designed to enforce traffic regulations, manage vehicle speeds, and ensure safer driving conditions throughout Lagos." – Oluwaseun Osiyemi, Commissioner of Transportation
As part of the Lagos Safe City initiative, the government has deployed 450 intelligent video cameras to monitor security and traffic around the clock. These cameras work alongside IoT sensors to gather data on traffic flow, vehicle speeds, and road conditions. Additionally, the state is incorporating AI-driven chatbots into the Lagos Digital Services Platform to streamline resident documentation processes and provide automated updates. This digital infrastructure is setting the stage for broader urban advancements.
Digital Connectivity and Urban Transformation
With its AI and IoT systems in place, Lagos is expanding its digital connectivity to transform urban services. In 2022, Lagos partnered with Huawei to implement AirEngine Wi-Fi 6 technology, creating a high-speed wireless network that boosts government efficiency. This effort complements the Metrofibre Project, which aims to lay 6,000 km (3,728 miles) of fiber optic cables by 2027. The first phase has already completed 2,700 km (1,678 miles) over three years.
This improved connectivity is driving down telecom costs and making internet access more affordable for both residents and businesses. The infrastructure supports 24/7 access to digital government services, such as e-taxation, health insurance through LASHMA, and education platforms like EKO EXCEL. Huawei has also introduced local cloud services in Nigeria, reducing data latency and ensuring compliance with data protection laws. This is a game-changer for small businesses and startups that rely on dependable and affordable digital infrastructure.
Environmental and Social Benefits
Smart city technologies are also helping Lagos tackle environmental issues while enhancing public safety. The Lagos State Waste Management Authority (LAWMA) is working on a project at the Olusosun landfill – a 100-acre site – to capture methane gas and convert it into electricity. The initiative is expected to generate 25 MW of power for the local grid, transforming Africa’s largest dump into a renewable energy source. Lagos produces around 14,000 tons of waste daily, yet only 40% is collected and 15% recycled. To address this, IoT-enabled waste bins equipped with real-time fill-level sensors are being tested to optimize collection routes and minimize pollution.
Optimized traffic systems are also reducing vehicle idling, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions and aligns with Lagos’ environmental targets. Further supporting innovation, the Lagos State Science Research and Innovation Council (LASRIC) has awarded over ₦800 million (roughly $530,000) in grants to more than 60 tech startups and 50 research projects, fostering solutions to urban challenges.
"The Sanwo-Olu administration’s vision goes beyond digital efficiency – it is about safeguarding lives, enhancing governance, and unlocking opportunity for every Lagosian." – Olatubosun Alake, Commissioner for Innovation, Science, and Technology
sbb-itb-dd089af
Job Creation and Economic Opportunities
Jobs in Technology and Infrastructure
The Digital Highway initiative is driving the creation of thousands of tech-related jobs. A key component of this effort, the Metrofibre Project, aims to lay 3,728 miles (6,000 km) of fiber optic cables by 2027, with 1,678 miles (2,700 km) already completed. This ambitious project has opened up opportunities in areas such as network engineering, cable installation, and system maintenance.
Additionally, the initiative has expanded technical support roles, particularly in cybersecurity and data privacy. The implementation of a 24-hour intelligent traffic enforcement system, supported by 450 surveillance cameras, requires skilled personnel for technical support, monitoring, and system administration. The integration of AI into various systems is also creating new roles for developers and data scientists.
To ensure that the workforce is ready to meet these demands, the Digital Leap Programme is training 50,000 Lagosians, aged 18 to 35, in advanced tech skills. Tunbosun Alake, the Commissioner for Science and Technology, emphasized the program’s goal: to equip young people with the tools to become problem solvers and contributors to Lagos’s growing innovation economy.
Economic Gains for SMEs and Startups
Beyond creating tech jobs, the Digital Highway is delivering clear economic advantages for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups. The expansion of the metro fiber network has significantly reduced internet deployment costs for telecom providers, which in turn lowers connectivity expenses for businesses. This makes it easier for startups to tap into a broader digital marketplace.
Real-time traffic monitoring, enabled by Intelligent Transportation Systems, offers logistics and e-commerce businesses a competitive edge. Smarter route planning and reduced congestion lead to lower fuel costs and faster delivery times – key factors for companies dependent on efficient transportation. Additionally, the digitization of government services, such as e-taxation and building permits, has streamlined processes, cutting down on bureaucratic delays that previously slowed small business operations.
"The PPP model allows Lagos government to spend less of taxpayer’s money and do more of the enabling environment that will help the private sector succeed in providing internet connectivity to the people of Lagos." – Mr. Olatunbosun Alake, Commissioner for Innovation, Science and Technology
Supporting Innovation in Lagos
The infrastructure improvements are not just about jobs and SME growth – they’re also sparking innovation across Lagos. The Lagos State Science Research and Innovation Council (LASRIC) has provided over ₦800 million in grants to more than 60 tech startups and 70 research initiatives. These grants empower entrepreneurs to tackle urban challenges without being solely dependent on private funding. Meanwhile, the forthcoming Lagos State Innovation Bill aims to solidify the state’s role as a hub for science and technology.
This digital transformation is also attracting major investments. The Abidjan–Lagos Corridor, which connects to Lagos’s digital framework, is expected to generate $16 billion in economic benefits and create 70,000 jobs. Entrepreneurs can leverage the Lagos Digital Services Platform for instant updates and essential documentation, while enhanced connectivity supports the growth of innovation hubs and co-working spaces throughout the city. The state’s proactive approach to AI governance and cybersecurity, including successfully thwarting two major data breaches, underscores its commitment to fostering a secure environment for tech-driven businesses.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Lagos
The Lagos Digital Highway is reshaping how the city operates, blending technology and infrastructure to address urban challenges. By 2027, the initiative aims to deploy 6,000 km (about 3,728 miles) of fiber optic cables, install 450 intelligent surveillance cameras, and provide training to 50,000 young Lagosians. These efforts are tackling issues like traffic congestion, poor connectivity, and unemployment all at once. So far, over 1 million residents have gained internet access, businesses are saving on internet deployment costs, and real-time traffic management is shortening commute times.
This progress is fueled by creative funding and implementation strategies. Central to this is the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model, which reduces the financial burden on taxpayers while speeding up deployment. As Commissioner Olatubosun Alake explained, "The PPP model allows Lagos government to spend less of tax payer’s money and do more of the enabling environment that will help the private sector succeed". Unified fiber-optic ducts, allowing multiple telecom providers to connect easily, further streamline this approach, creating a model that other cities can replicate.
Lagos is setting a new benchmark by integrating physical infrastructure with digital services into a unified digital system. Cybersecurity has been a cornerstone of this transformation, with measures like preventing major data breaches and employing over 100 certified Data Protection Officers. This ensures the foundation is secure as the city continues to grow digitally.
For other African cities, Lagos offers a practical roadmap. Strategies such as integrating unified infrastructure during road construction, establishing reliable digital identity systems (with 6 million residents already registered under LASRRA), and linking infrastructure projects with talent development programs are proving effective. Policies like the Lagos State Innovation Bill and emerging AI governance guidelines further ensure this growth is both forward-thinking and secure. Together, these efforts position Lagos as a model for tackling urban challenges.
The economic ripple effects of this initiative extend far beyond the city itself. The Abidjan–Lagos Corridor, which connects to this digital framework, is expected to generate $16 billion in economic benefits and create 70,000 jobs. As Commissioner Alake highlighted, "The Sanwo-Olu administration’s vision goes beyond digital efficiency – it is about safeguarding lives, enhancing governance, and unlocking opportunity for every Lagosian". By combining digital infrastructure with practical services and strong cybersecurity, Lagos is building a foundation for long-term urban prosperity and demonstrating how smart city solutions can scale effectively.
FAQs
How does the Lagos Digital Highway help ease traffic congestion in the city?
The Lagos Digital Highway aims to ease traffic congestion by introducing a cutting-edge digital traffic management system. This system relies on smart cameras and sensors strategically placed across the city to monitor traffic conditions in real time, enforce speed limits, and identify violations. With access to live data, authorities can respond quickly to incidents, adjust traffic signals as needed, and streamline the flow of vehicles.
A key part of this initiative is the expansion of Lagos’s fiber optic network, which enhances communication between traffic systems and speeds up data sharing. This improved connectivity not only helps coordinate traffic more efficiently but also reduces delays and boosts emergency response times. The project represents a significant move toward a more interconnected and efficient urban infrastructure, supporting Lagos’s vision of becoming a smart city.
What kinds of jobs are being created by the Lagos Digital Highway project?
The Lagos Digital Highway project is opening up a variety of job opportunities across several industries. In construction and engineering, the push to build road networks, install fiber optic systems, and implement smart traffic solutions is creating a surge in demand for skilled professionals. These activities are expected to result in thousands of direct jobs.
In the tech world, the project is paving the way for roles like IT specialists, data analysts, cybersecurity experts, and software developers. With the integration of smart city technologies such as real-time traffic monitoring and AI-driven platforms, the need for tech talent is growing. Beyond just filling jobs, the initiative is also fueling innovation by backing research projects and startups, encouraging entrepreneurship, and opening doors to new possibilities in technology and urban management.
This project is doing more than just upgrading Lagos’s infrastructure – it’s becoming a catalyst for job creation in construction, technology, and forward-thinking industries.
How will the fiber-optic expansion improve life for Lagos residents and businesses?
The ongoing expansion of Lagos’ fiber-optic network is reshaping how the city stays connected, delivering faster and more dependable internet access across the region. With over 6,000 kilometers of fiber-optic cables already in place and an additional 1,200 kilometers planned by 2025, this project is making online access more seamless for residents. This means smoother remote work, easier use of digital platforms, and better availability of online services.
For businesses, this upgraded network lays the groundwork for advancements like smart city technologies, robust data centers, and enhanced cybersecurity measures. It also sparks economic growth by encouraging telecom providers to broaden their offerings, potentially driving down internet costs and improving service quality. These developments are steering Lagos toward becoming a more connected and forward-thinking city, aligning with its goal of emerging as a leading smart city in Africa.
Related Blog Posts
- African Tech Hub Comparison: Lagos vs Nairobi vs Cape Town
- Top African Startups in Public Transport Monitoring
- Smart Cities in Africa: Economic Benefits Explained
- How AI Improves Logistics for African Startups





